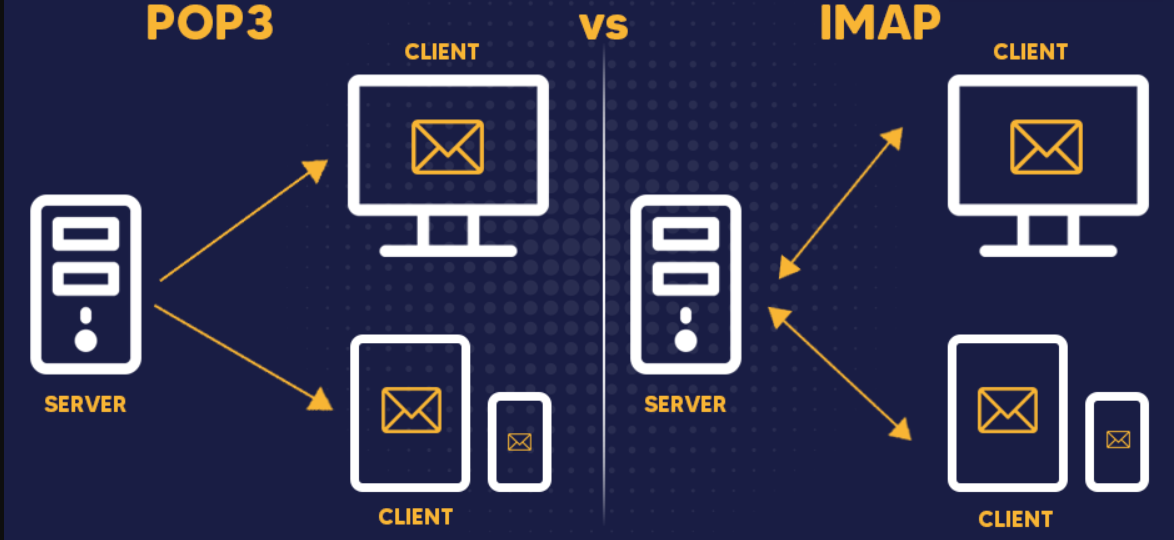
POP3 and IMAP both are two different email protocols used for retrieving emails from a mail server to a local device such as a computer or a smartphone. If you are about to setup and email service like outlook, thunderbird, etc… there is no doubt you will come across the options like POP3 and IMAP.
In this blog we are going to find out the difference between email clients & webmail, what is POP3 and IMAP and common differences between.
Table of Contents
Email Clients vs Webmail
Email clients and webmail are two different methods of accessing and managing email, each with its own set of advantages. Here’s a comparison between email clients and webmail.
Email Clients
- Definition:
- Email clients are software applications installed on a local device (such as a computer or smartphone) that allow users to manage their email accounts.
- Examples of email clients include Microsoft Outlook, Mozilla Thunderbird, Apple Mail, and others.
- Storage:
- Email clients often download emails to the local device, which can save storage space on the email server.
- Emails are stored locally, making them accessible even without an internet connection.
- User Interface:
- Email clients typically provide a more feature-rich and customizable user interface.
- They often offer advanced features like offline access, advanced filtering, and integration with other applications.
- Integration:
- Email clients can be integrated with other software and services, providing a more comprehensive toolset for productivity.
- Privacy and Security:
- Some users prefer email clients for privacy reasons, as emails are stored locally, and there is less reliance on external servers.

Webmail
- Definition:
- Webmail refers to the use of a web browser to access and manage emails through a web-based email service.
- Examples of webmail services include Gmail, Yahoo Mail, Outlook.com, and others.
- Accessibility:
- Webmail is accessible from any device with an internet connection and a web browser. There is no need to install additional software.
- It provides a convenient way to access emails from different locations and devices without the need for synchronization.
- Storage:
- Emails are stored on the email server, and users access them through the web interface. This means that the storage space is managed on the server side.
- Webmail services often offer large storage quotas, eliminating concerns about running out of space.
- Updates and Maintenance:
- Webmail services are maintained and updated by the email service provider. Users don’t need to worry about installing updates or managing software on their local devices.
- Collaboration:
- Webmail often integrates seamlessly with other online services and collaboration tools, making it easy to share documents, schedule events, and collaborate with others.
Ultimately, the choice between email clients and webmail depends on individual needs, preferences, and the specific features required for managing email. Many users find a combination of both approaches beneficial based on their use cases and requirements.
What Is POP3?
POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol 3, is a standard email protocol used for receiving emails from a mail server to a local email client. It is one of the most common email retrieval protocols, especially for personal email accounts.
POP3 is designed to download emails from the mail server to the local device (e.g., computer or smartphone). It typically operates as a one-way communication, meaning that actions performed on the local email client (such as reading or deleting emails) do not affect the original emails on the mail server. Once emails are downloaded to the local device, users can access them offline without an internet connection.
It’s important to note that when using POP3, care should be taken to ensure that emails are backed up since they are typically removed from the server after being downloaded. If a user loses their local copy of the emails, they might not be retrievable from the server.
What Is IMAP?
In contrast to POP3, IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is another email protocol that allows for two-way communication and synchronization across multiple devices, making it more suitable for users who access their emails from different locations and devices.
IMAP is a standard email protocol used for retrieving and managing emails from a mail server. Unlike POP3 which primarily downloads emails to a local device, IMAP is designed to provide a more flexible and synchronized email experience across multiple devices.
IMAP is particularly beneficial for users who access their emails from multiple devices, as it ensures that the same set of emails and their status (read/unread, deleted, etc.) is consistent across all devices. It is commonly used for professional and business email accounts where collaboration and synchronization are essential.
Other Email Protocols
Yes, in addition to POP3 and IMAP, there are several other email protocols that serve various purposes in the realm of email communication. but the vast majority of people use one of the three major protocols— POP3 and IMAP. Since these technologies likely cover the needs of nearly all our readers, we are not going to delve deep into the other protocols.
However apart from the major once like POP3 and IMAP, here is the few here are a few notable ones:
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
- Exchange ActiveSync
- MAPI (Messaging Application Programming Interface)
- LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
- POP4
- CalDAV and CardDAV
- OAuth (Open Authorization)
- Webhooks and APIs
It’s important to note that the choice of protocols may depend on the email service provider and the specific requirements of the user or organization. Different protocols offer varying levels of functionality, security, and compatibility with different email clients and devices.
Common Differences Between POP3 and IMAP
The differences between POP3 and IMAP are significant and impact how emails are managed, accessed, and stored. Here are some common differences between POP3 and IMAP:
- Email Retrieval:
- POP3: Downloads emails from the mail server to the local device and typically removes them from the server.
- IMAP: Retrieves and manages emails directly on the mail server. Emails are not automatically removed from the server when downloaded.
- Storage Location:
- POP3: Stores emails on the local device, making them accessible offline. The server acts as a temporary repository until the emails are downloaded.
- IMAP: Keeps emails on the mail server. The email client acts as a window to view and manage emails stored on the server.
- Synchronization:
- POP3: Operates as a one-way communication. Changes made on the local device (e.g., marking an email as read) do not affect the server or other devices.
- IMAP: Supports two-way communication. Changes made on one device (e.g., marking an email as read or deleted) are reflected on the server and other connected devices.
- Offline Access:
- POP3: Allows offline access to downloaded emails on the local device. Changes made offline are not synchronized with the server until the next connection.
- IMAP: Also allows offline access by caching a copy of emails on the local device. Changes made offline are synchronized with the server when a connection is reestablished.
- Multiple Device Access:
- POP3: Less suitable for users who access their email accounts from multiple devices, as changes are not synchronized across devices.
- IMAP: More suitable for users who access their email from multiple devices, as changes are synchronized across all devices.
- Email Backup:
- POP3: Users need to ensure proper backup of emails since they are typically removed from the server after being downloaded.
- IMAP: Emails remain on the server, providing a form of backup in case a local device is lost or fails.
- Server Space Usage:
- POP3: Can help in managing server space as emails are removed from the server after being downloaded.
- IMAP: Uses server space to store emails, but this provides a backup in case a local device is lost or fails.
- Configuration:
- POP3: Requires configuration with settings such as server address, port numbers, and security settings.
- IMAP: Also requires configuration with similar settings, but it offers more options for synchronization.
Finally, the choice between POP3 and IMAP depends on individual preferences and requirements, such as the need for offline access, multiple device synchronization, or server space management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between POP3 and IMAP depends on your specific needs and how you prefer to manage your email. Here’s a summary of the key points:
POP3:
- Downloads emails from the server to the local device.
- Typically removes emails from the server after downloading.
- One-way communication: Changes made on the local device do not affect the server.
- Suitable for users who primarily use one device for email and want offline access.
IMAP:
- Manages emails directly on the server.
- Does not automatically remove emails from the server when downloaded.
- Two-way communication: Changes made on one device are reflected on the server and other connected devices.
- Suitable for users who access their emails from multiple devices and require synchronization.
Considerations:
- If you prefer offline access and a local copy of your emails, POP3 may be suitable.
- If you use multiple devices and want consistent access to emails across them, IMAP is a better choice.
- IMAP provides a backup on the server, while POP3 requires users to manage backups locally.
- Security measures like SSL/TLS can be applied to both POP3 and IMAP to encrypt the communication.
Ultimately, the best choice between POP3 and IMAP depends on your workflow, the number of devices you use, and your preferences regarding email storage and accessibility. Additionally, keep in mind that modern email services often offer both POP3 and IMAP support, allowing you to choose the protocol that aligns with your specific requirements.
If you are looking for hosting service which provide BulkSpace and both POP3 and IMAP for you to choose, make sure to check out our website, which we provide from shared to dedicated servers for you to choose from.