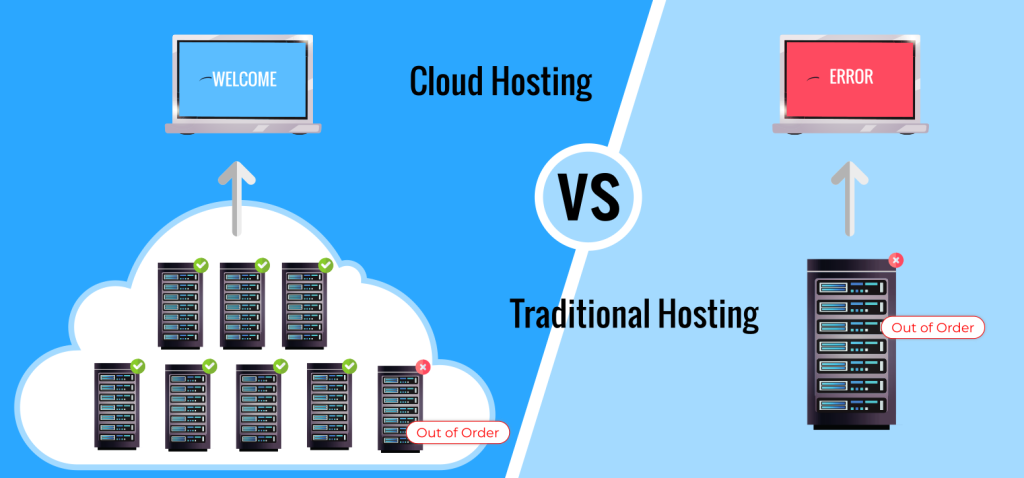
Cloud Hosting Vs Traditional Hosting both are different approaches to hosting and managing websites, applications, and other online services.
In this post, we’ll take a look at what each hosting service has to offer, including their pros and cons, so that you can weigh-up your options. And then, we’ll share three of the best cloud and traditional hosting providers to help you narrow your selection.
Table of Contents
What Is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting service that utilizes a network of remote servers to store, manage, and deliver data and applications over the internet. Instead of relying on a single physical server or a dedicated server in a specific location, cloud hosting distributes the resources across multiple interconnected servers that form a virtualized environment.
Cloud hosting is a relatively new kind of hosting, but it’s becoming more popular as it has several benefits over traditional hosting.
Cloud hosting allows users to easily scale their resources up or down based on their needs. Also, providers maintain a pool of computing resources (CPU, memory, storage) that is shared among multiple users. Resources are dynamically allocated to meet the changing demands of users and applications.
What Is Traditional Hosting?
Traditional hosting, often referred to as on-premises hosting or dedicated hosting, involves the use of physical servers and infrastructure located in a specific data center or on-site within an organization’s premises. Unlike cloud hosting, where resources are distributed across a network of remote servers, traditional hosting relies on dedicated hardware that is owned or leased by the hosting user.
While cloud hosting has gained popularity for its flexibility and scalability, traditional hosting remains in use, especially in scenarios where specific control over hardware and infrastructure is a priority, or where regulatory requirements dictate on-premises hosting. Some businesses may also adopt a hybrid approach, combining elements of both traditional and cloud hosting to meet their specific needs.
The main differences between cloud hosting VS traditional hosting
The main differences between cloud hosting vs traditional hosting lie in their infrastructure, scalability, resource allocation, cost structure, and management. Here’s a summary of these key distinctions:
- Infrastructure:
- Cloud Hosting: Utilizes a network of remote servers, often spread across multiple data centers. Virtualization technologies create virtual instances of servers, allowing for flexibility and resource optimization.
- Traditional Hosting: Involves physical servers located in a specific data center or on-premises. Dedicated hardware is used for hosting, and the infrastructure is typically fixed.
- Scalability:
- Cloud Hosting: Easily scalable on-demand. Resources can be increased or decreased based on demand, providing flexibility and cost-efficiency.
- Traditional Hosting: Scalability may be more limited, often requiring manual intervention to add or upgrade physical hardware.
- Resource Allocation:
- Cloud Hosting: Resources are dynamically allocated from a shared pool. Virtualization allows for efficient utilization of resources and the ability to scale horizontally.
- Traditional Hosting: Resources are allocated on a per-server basis. Each physical server is dedicated to specific tasks, and resource sharing may be less flexible.
- Cost Structure:
- Cloud Hosting: Typically operates on a pay-as-you-go or pay-per-use model. Users pay for the resources they consume, providing flexibility and cost efficiency.
- Traditional Hosting: Involves fixed costs, where users pay for the entire infrastructure, regardless of actual resource usage. This can be less cost-effective for variable workloads.
- Redundancy and Reliability:
- Cloud Hosting: Often incorporates redundancy at various levels (servers, data centers, geographic locations), enhancing reliability and availability.
- Traditional Hosting: Reliability depends on the quality and redundancy of the physical infrastructure. Failures or issues with hardware can impact availability.
- Management and Control:
- Cloud Hosting: Offers managed services, allowing users to offload responsibilities such as maintenance, security, and updates. Users have less direct control over the underlying infrastructure.
- Traditional Hosting: Users have more direct control over physical servers and infrastructure. They are responsible for server maintenance, security, and updates.
- Global Accessibility:
- Cloud Hosting: Enables users to access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting global accessibility.
- Traditional Hosting: Accessibility is limited to the physical location of the hosting infrastructure, potentially leading to slower access for geographically distant users.
In summary, cloud hosting is characterized by its flexibility, scalability, and dynamic resource allocation, operating on a variable cost structure. Traditional hosting, on the other hand, involves fixed infrastructure, may have limited scalability, and offers more direct control over physical servers.
The choice between the two depends on specific requirements, preferences, and the nature of the workloads being hosted. Many organizations today may adopt a hybrid approach, combining elements of both cloud and traditional hosting for optimal performance and flexibility.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting offers various advantages and disadvantages, and the decision to use it depends on specific business needs, budget constraints, and technical requirements. Here are some pros and cons of cloud hosting:
Pros of Cloud Hosting:
- Scalability:
- Pro: Easy scalability allows users to quickly scale up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal resource utilization and cost efficiency.
- Flexibility:
- Pro: Cloud hosting provides flexibility in terms of resource allocation, allowing users to adapt to changing requirements and workloads.
- Cost Efficiency:
- Pro: Pay-as-you-go pricing models mean users only pay for the resources they consume, which can be cost-effective for variable workloads.
- Redundancy and Reliability:
- Pro: Cloud hosting often incorporates redundancy at various levels, reducing the risk of downtime due to hardware failures or other issues.
- Global Accessibility:
- Pro: Users can access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, making it suitable for distributed teams and global operations.
- Managed Services:
- Pro: Cloud providers offer a range of managed services, offloading responsibilities such as maintenance, security, and updates from users.
- Rapid Deployment:
- Pro: Cloud services can be provisioned quickly, allowing for rapid deployment of applications and services.
- Innovation:
- Pro: Cloud providers often introduce new technologies and features, allowing users to leverage the latest innovations without significant upfront investments.
Cons of Cloud Hosting:
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity:
- Con: Access to cloud resources relies on internet connectivity. Issues with the internet can impact service availability.
- Security Concerns:
- Con: Some organizations are hesitant to move sensitive data to the cloud due to security and privacy concerns. However, cloud providers invest heavily in security measures.
- Potential for Downtime:
- Con: While cloud providers aim for high availability, downtime can still occur due to issues like outages, maintenance, or misconfigurations.
- Variable Costs:
- Con: While the pay-as-you-go model can be cost-effective, it may result in variable and potentially unpredictable monthly expenses.
- Limited Control:
- Con: Users have less direct control over the underlying infrastructure in a cloud environment compared to on-premises solutions.
- Data Transfer Costs:
- Con: Some cloud providers may charge for data transfer between different regions or services, which can contribute to additional costs.
- Integration Challenges:
- Con: Integrating existing on-premises systems with cloud services may present challenges, especially for complex or legacy applications.
- Potential Vendor Lock-In:
- Con: Depending heavily on a single cloud provider may lead to vendor lock-in, making it challenging to switch providers or move services back on-premises.
It’s important for organizations to carefully evaluate their specific needs and conduct a cost-benefit analysis when considering cloud hosting. Many businesses adopt a hybrid or multi-cloud approach to combine the benefits of cloud hosting with on-premises solutions.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Hosting
Traditional hosting, also known as on-premises hosting or dedicated hosting, comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The suitability of traditional hosting depends on factors such as control requirements, security considerations, and the specific needs of the organization. Here are some pros and cons of traditional hosting:

Pros of Traditional Hosting:
- Direct Control:
- Pro: Users have direct control over the physical servers and infrastructure, allowing for customization of hardware specifications and software configurations.
- Predictable Costs:
- Pro: Traditional hosting often involves fixed costs, providing predictability in budgeting as users pay for the entire infrastructure regardless of resource usage.
- Security Oversight:
- Pro: Users have greater control over security measures, enabling them to implement specific security protocols and measures tailored to their needs.
- Physical Access:
- Pro: Having physical control over servers allows for easier physical access and hands-on management, which can be advantageous for troubleshooting or maintenance.
- No Dependency on Internet Connectivity:
- Pro: Access to hosted resources is not dependent on internet connectivity, which can be crucial in certain scenarios where reliable internet access is a concern.
- Customization:
- Pro: Greater flexibility in terms of customizing hardware components and configurations to meet specific application or workload requirements.
Cons of Traditional Hosting:
- Limited Scalability:
- Con: Traditional hosting may have limitations in scalability, making it challenging to quickly adapt to changing resource demands, especially during traffic spikes.
- High Upfront Costs:
- Con: Acquiring and maintaining physical hardware involves significant upfront costs for purchasing servers, networking equipment, and other infrastructure components.
- Resource Inefficiency:
- Con: Fixed resource allocation may result in underutilization of hardware, especially during periods of low demand, leading to inefficient resource use.
- Maintenance and Upkeep:
- Con: Users are responsible for server maintenance, updates, and security, which can be time-consuming and require technical expertise.
- Limited Redundancy:
- Con: Redundancy measures may be more challenging to implement, increasing the risk of downtime in the event of hardware failures.
- Geographical Limitations:
- Con: The physical location of the hosting infrastructure limits accessibility and can result in slower response times for geographically distant users.
- Long Deployment Times:
- Con: Setting up and deploying new servers in a traditional hosting environment may take longer compared to the rapid provisioning available in cloud hosting.
- Scalability Challenges:
- Con: Adding resources or upgrading hardware in a traditional hosting setup may involve manual processes and downtime.
Organizations need to carefully weigh these pros and cons when deciding between traditional hosting and other hosting options, such as cloud hosting. In some cases, a hybrid approach that combines elements of both traditional and cloud hosting may be the most suitable solution.
Wrapping up
Certainly! To wrap up: Cloud hosting won’t suit everyone.
In some cases, traditional hosting works fine. There’s nothing wrong in starting with a traditional shared hosting service. It’s only when you’re ready to step up to more powerful web hosting that you need to consider cloud hosting.
- Cloud Hosting:
- Pros:
- Scalability: Easily scalable resources based on demand.
- Flexibility: Dynamic resource allocation and adaptability.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go model for cost-effectiveness.
- Redundancy: Often includes redundancy for high availability.
- Global Accessibility: Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cons:
- Dependency on Internet: Access reliant on internet connectivity.
- Security Concerns: Potential concerns, but providers invest in security.
- Variable Costs: Costs can be variable and potentially unpredictable.
- Limited Control: Users have less direct control over infrastructure.
- Pros:
- Traditional Hosting:
- Pros:
- Direct Control: Full control over physical servers and infrastructure.
- Predictable Costs: Fixed costs for predictable budgeting.
- Security Oversight: Greater control over security measures.
- No Internet Dependency: Access not dependent on internet connectivity.
- Cons:
- Limited Scalability: Challenges in quickly adapting to resource demands.
- High Upfront Costs: Significant upfront costs for physical hardware.
- Resource Inefficiency: Fixed resource allocation may lead to inefficiency.
- Maintenance Burden: Users are responsible for maintenance and security.
- Pros:
Choosing between Cloud hosting VS Traditional hosting depends on the specific needs, preferences, and characteristics of the workload or application. Many organizations today adopt a hybrid or multi-cloud approach to leverage the benefits of both hosting models. Considerations include scalability requirements, budget constraints, control preferences, and the level of technical expertise available within the organization.