Among all the best virtualization technologies available, KVM virtualization stands out due to its performance, integration, and flexibility with the Linux kernel.
This open-source virtualization is playing its role to enhance the capabilities of businesses to meet the evolving demands of the digital era. The introduction of KVM has made developer’s work easy and has improved the development cycle as well. This article will explore KVM virtualization and its advantages on VPS Hosting easily. You will be able to understand how virtualization fosters collaboration and continuously improves performance.
Table of Contents
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization is a superpower technology that creates software-based versions of physical computing resources. It allows a computer to do multiple computer’s jobs and creates a single computer within a computer. It can run many operating systems and applications on a single server in a secure environment. Virtualization is the foundation of cloud computing and improves efficiency, flexibility and resource utilization.
What is KVM Virtualization?
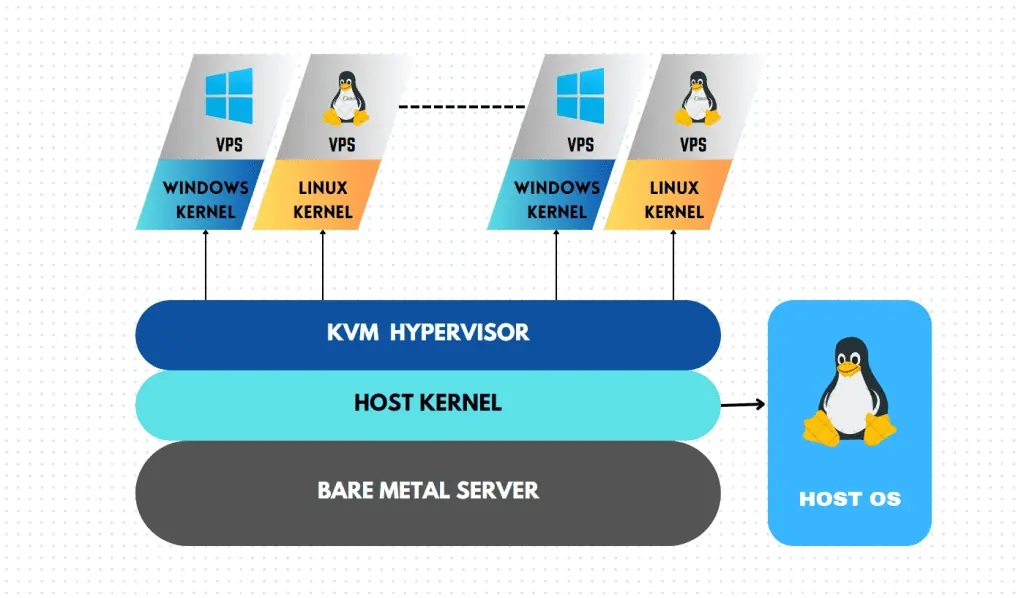
KVM (Kernel-Based Virtual Machine) is an open-source virtualization technology. It has been a part of the Linux kernel since 2007 and is a full-virtualization module that lets you turn Linux into a hypervisor. It helps the host run multiple isolated virtual machines
The KVM is a part of Linux code, so it automatically benefits from all the new features, fixes, and advancements of Linux.

Features of KVM Virtualization
Let’s check out the features of KVM Virtualization, which make it an enterprise’s preferred hypervisor.
- Enhanced security and isolation
- Improved storage and provides redundancy
- Utilize a wide variety of certified Linux-supported hardware platforms
- Reliable memory management for better performance
- Supports live migration
- Fair scheduling and resource control
- Better prioritization make sure apps are running accordingly
- CPU Hotplug support – Adding CPUs on the fly
- KVM Paravirtual Clock – A paravirtual time source for KVM
- PCI Hotplug support – Adding PCI devices on the fly
- VM channel-Communication channel between the host and guests
- Nested Guests – Running virtual machines within virtual machines
What is a KVM VPS?
KVM is a virtualization solution for Linux that allows the hosting of various virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. With KVM virtualization, each VM operates as an independent entity with its own virtualized hardware resources like memory, CPU, and disk space.
A KVM VPS offers several benefits:
- Isolation: Each KVM VPS is isolated from other VMs on the same physical server. This ensures that the performance and security of one VPS are independent of activities of others.
- Full root access: KVM VPS provides full administrative access which allows users to have control over their virtual server. This helps users to install and configure their preferred operating system, software applications, and settings.
- Dedicated resources: KVM VPS offers dedicated resources to each virtual machine, meaning that the allocated CPU, memory, and disk space are not accessible to other users. This assures consistent performance and eliminates the risk of resource contention.
- Scalability: KVM VPS can be seamlessly scaled up or down based on the user’s requirements. Additional resources, such as CPU cores, RAM, and storage, can be modified as needed, providing flexibility and cost-efficiency.
KVM VPS provides a reliable and customizable virtual server environment that allows users to run their applications and websites with the help of virtualization technology.
The Advantages of KVM Virtualization
1. Performance
KVM offers excellent performance due to its efficient integration with the Linux kernel and hardware virtualization extensions. It allows direct access to host hardware resources, resulting in low latency and high throughput for virtual machines. KVM’s performance is comparable to running applications natively on the host machine.
2. Full Virtualization
KVM provides full virtualization capabilities, allowing you to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) with different operating systems on a single host. Each VM runs its own independent kernel, enabling you to use a wide range of operating systems, including Linux, Windows, BSD, and others.
3. Scalability
KVM is an established virtualization solution with a stable codebase and long history of development. It benefits from being a part of the Linux kernel, which provides continuous updates, security patches, and widespread hardware compatibility. It is widely adopted and trusted by many organizations and enterprises.
4. Resource Efficiency
KVM enables efficient resource allocation and utilization. It provides granular control over resource allocation, allowing administrators to allocate CPU cores, memory, storage, and network bandwidth to VMs as needed. KVM also supports overcommitting resources, where the total allocated resources can exceed the physical capacity, leveraging the assumption of not all VMs use their allocated resources fully at the same time.
5. Security and Isolation
KVM provides enhanced security through isolation between virtual machines. Each VM runs its kernel and operates in its isolated environment, which helps prevent one VM from affecting others. Additionally, KVM benefits from the security features provided by the underlying Linux kernel, such as SELinux and mandatory access controls.
6. Open-Source and Ecosystem Support
KVM is an open-source technology with the support of a large community of developers and contributors. This active community ensures continuous improvement, bug fixes, and the availability of various tools and resources to support KVM deployment and management. It also enjoys support from major industry players, such as Red Hat, which provides commercial solutions and ecosystem support around KVM.
7. Cloud Compatibility
KVM is made use of by cloud platforms and infrastructure providers, including OpenStack. Its compatibility with cloud environments allows for seamless deployment and management of virtual machines in cloud infrastructures.