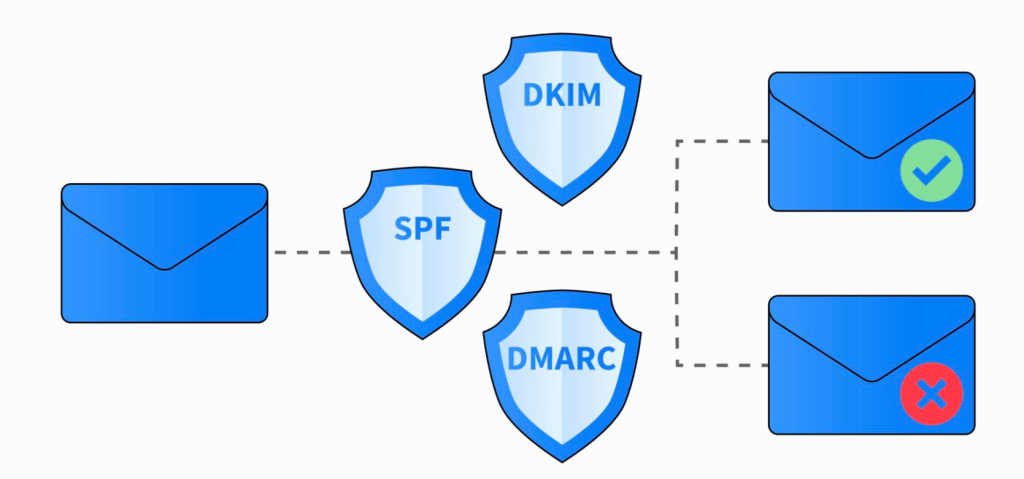
SPF and DKIM records are both email authentication mechanisms designed to enhance the security and reliability of email communication by preventing email spoofing and phishing attacks. They work together to help verify the legitimacy of the sender’s domain.
Your website and custom domain-based email are the two most important representations of your business. Even though there are multiple methods to contact your customers / clients email remains the most reliable mode of communication. The success of the communication is highly dependent on the delivery of the email to the intended recipients.
Here SPF and DKIM records acts as the essential components of email authentication, providing an additional layer of security and trust for email communication by preventing unauthorized use of domains and ensuring the integrity of email messages.
Table of Contents
How can you ensure better email delivery?
Email deliverability of your domain-based mail depends on the Spam checks done at the recipient end. Basic checks done by the recipient servers are the SPF and DKIM validations.
Ensuring better email delivery involves implementing best practices to optimize the chances of your emails reaching recipients’ inboxes and avoiding spam filters. Implementing DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance), SPF and DKIM, to authenticate your emails. This helps prevent email spoofing and enhances your domain’s reputation.
What is SPF record?
A Sender Policy Framework (SPF) record is a type of DNS (Domain Name System) record that specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of a specific domain. SPF is an email authentication protocol designed to prevent email spoofing and phishing attacks by allowing domain owners to declare which servers are legitimate senders for their domain.
The SPF record is published in the DNS settings of the domain and contains information about the mail servers that are authorized to send emails on behalf of that domain. When an email is received, the recipient’s mail server can check the SPF record of the sender’s domain to verify the authenticity of the sending server.
It’s important for domain owners to create and maintain accurate SPF records to ensure proper email authentication. SPF records are one component of a comprehensive email authentication strategy, often used in conjunction with DKIM and DMARC for enhanced security.
What is DKIM record?
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method that allows the sender to digitally sign the email content. This digital signature helps verify that the email has not been altered or tampered during transit and ensures the authenticity of the sender’s domain.
A DKIM record is a DNS record associated with a domain, containing information necessary for email receivers to verify the DKIM signature. The record includes a public key that corresponds to a private key held by the email sender. The private key is used to create the digital signature, while the public key is published in the DNS to allow email receivers to verify the signature.
When an email is sent, the sender’s mail server signs the email using its private key, and the recipient’s mail server can use the public key from the DKIM DNS record to verify the signature. If the verification is successful, it means that the email has not been altered in transit and is likely from the claimed sender.
Implementing SPF and DKIM along with other email authentication mechanisms like DMARC, helps enhance email deliverability and security by preventing email spoofing and phishing attacks.
What is DMARC?
DMARC, stands for “Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance,” is an email authentication and reporting protocol. DMARC builds on the existing SPF and DKIM authentication mechanisms, providing a framework for domain owners to specify how their emails should be authenticated and what action receivers should take if authentication fails.
The primary goals of DMARC are to:
- Authenticate Emails: DMARC enables domain owners to declare their email authentication practices, specifying which authentication methods (SPF and DKIM) they use and how receivers should handle emails that fail authentication.
- Improve Email Deliverability: By providing clear instructions to email receivers on how to handle unauthenticated emails, DMARC helps prevent domain spoofing and phishing attacks. It also enhances the chances of legitimate emails being delivered to recipients’ inboxes.
- Receive Reporting: DMARC includes reporting mechanisms that allow domain owners to receive feedback on the authentication results of their emails. These reports provide insights into how their domain is being used and help identify potential issues.
Implementing DMARC, along with SPF and DKIM, provides a comprehensive email authentication strategy, enhancing the security of email communication and reducing the likelihood of phishing attacks using the domain.
Why are SPF and DKIM records important for your domain?
SPF and DKIM records are important for your domain for several reasons, as they play crucial roles in ensuring the security, authenticity, and deliverability of your email communications.
Here are some of the reasons why SPF and DKIM records important:
- Preventing Email Spoofing:
- SPF and DKIM help prevent email spoofing, where malicious actors send emails that appear to be from a legitimate domain. SPF specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain, and DKIM provides a digital signature to verify the authenticity of the email content.
- Enhancing Email Deliverability:
- Email providers use SPF and DKIM records to authenticate incoming emails. Having properly configured and maintained SPF and DKIM records increases the likelihood that your emails will be delivered to recipients’ inboxes rather than being flagged as spam or rejected.
- Building Sender Reputation:
- Sender reputation is a critical factor in email deliverability. SPF and DKIM contribute to building and maintaining a positive sender reputation by demonstrating to email providers that your domain takes measures to authenticate and secure its emails.
- Reducing False Positives:
- Without SPF and DKIM records, legitimate emails from your domain may be incorrectly marked as spam or phishing attempts. By implementing these authentication mechanisms, you reduce the chances of false positives and ensure that your legitimate emails are recognized as such.
- Protecting Against Phishing Attacks:
- Phishing attacks often involve the use of forged email headers and content to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information. SPF and DKIM help protect against such attacks by verifying the legitimacy of the sender and ensuring the integrity of the email content.
- Compliance with Best Practices and Standards:
- Many email providers and industry standards recommend or require the use of SPF and DKIM for proper email authentication. Adhering to these best practices and standards helps ensure that your emails are accepted and trusted across different email platforms.
- Monitoring and Reporting:
- Both SPF and DKIM offer reporting mechanisms that provide insights into email authentication results. Monitoring these reports allows you to identify issues, such as unauthorized use of your domain or failed authentication attempts, and take corrective actions.
- Comprehensive Email Authentication:
- SPF, DKIM, and DMARC together form a comprehensive email authentication framework. DMARC builds on SPF and DKIM, providing additional policies and reporting capabilities to further enhance email security and control.

Having the SPF and DKIM records configured for your domain is also important in light of the recent announcement by Google and Yahoo to make email authentication a mandatory requirement for bulk email senders to their recipients starting in February 2024. It’s likely that the same requirement will eventually be extended to one-to-one business email communication as well.
In summary, SPF and DKIM records are essential components of a robust email authentication strategy. They help protect your domain from unauthorized use, improve email deliverability, and contribute to the overall security and trustworthiness of your email communications.